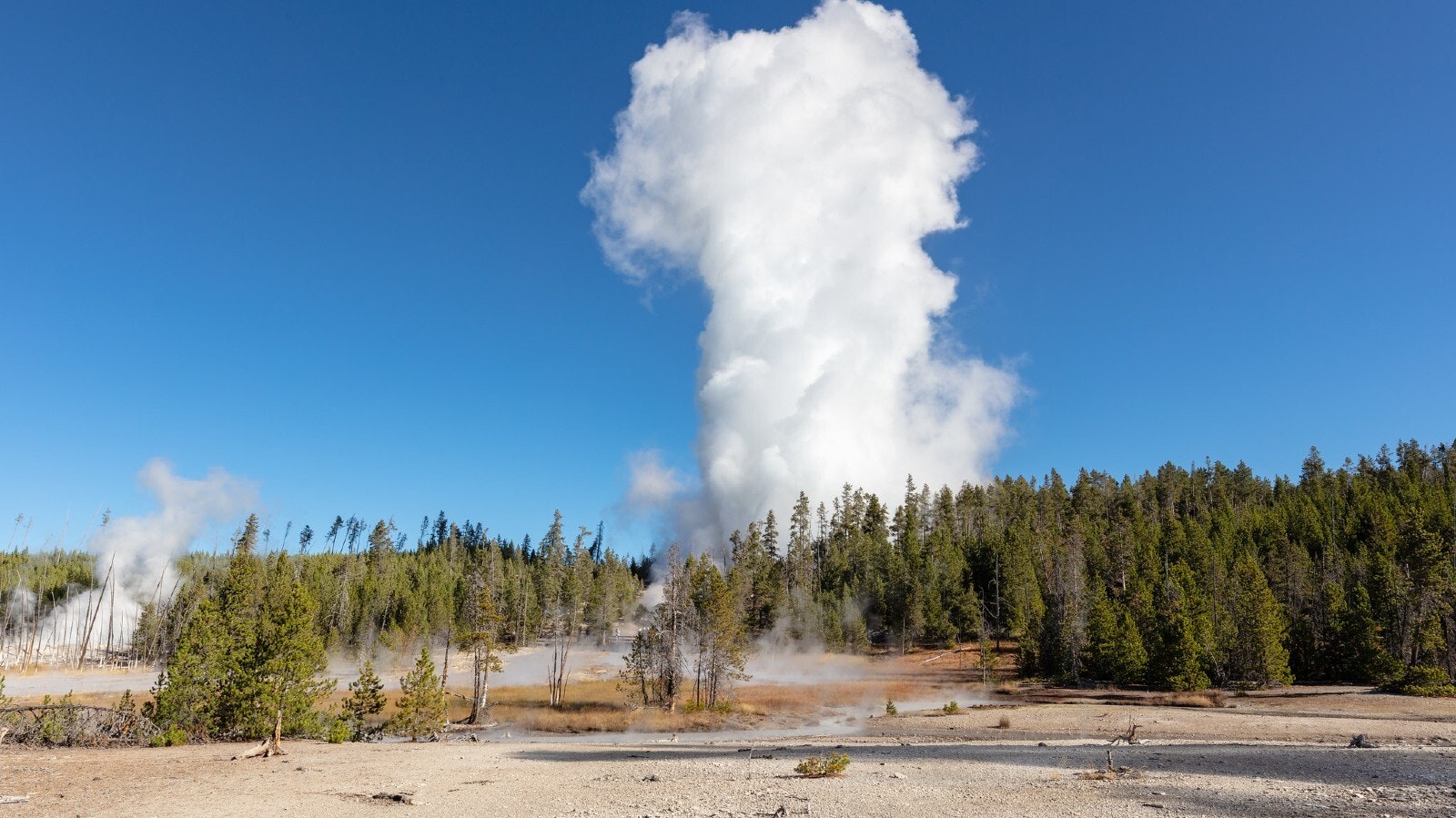
One of Yellowstone Park’s main attractions, the Steamboat Geyser, is getting quieter, and might be going into a long period of dormancy, a geophysicist said.
“We always knew that this period of frequent eruptions was going to come to an end. We don’t know exactly when that end will be,” Michael Poland told Cowboy State Daily. He’s a research geophysicist at the U.S. Geological Survey’s Cascades Volcano Observatory and the scientist-in-charge of the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory.
The geyser was highly active from 2018 until June of this year, sometimes erupting several times a month. But it’s now been more than two months since its last eruption, Poland said.
Steamboat is the world’s tallest active geyser; it’s biggest eruptions can hit 300 feet in height. It’s one of about 500 geysers in the park. While the Old Faithful geyser has highly predictable eruptions, most other geysers, including Steamboat, are sporadic, Poland said.
A History Of Boom-Bust Cycles
Steamboat has a history of going dormant, punctuated by periods of brisk activity, Poland said. It’s thought to have gone completely dormant for nearly 50 years, starting in the 1910s. It had bursts of activity during the 1960s and 1980s. Its last extended dormant period was between September 2014 until March 2018, he said.
It’s not certain whether the current slowdown means Steamboat could be entering another years-long, or even decades-long, dormant period, Poland said.
“It may not be going completely back to sleep yet,” he said. “It is having these persistent low-level eruptions, where the water is splashing just a few feet above the vent.”
Unknown Lifespan
It’s also nearly impossible to determine just how long Steamboat, or any Yellowstone Geyser, will last until it goes completely quiet forever, Poland said.
However, on the geological time scale, it could still be considered “new”, he said.
“Yellowstone was completely glaciated about 14,000 years ago, and when those ice sheets finally melted, that wiped the slate clean,” he said. “All of these geyser features – the cones and vents themselves – are new since that last ice age.”